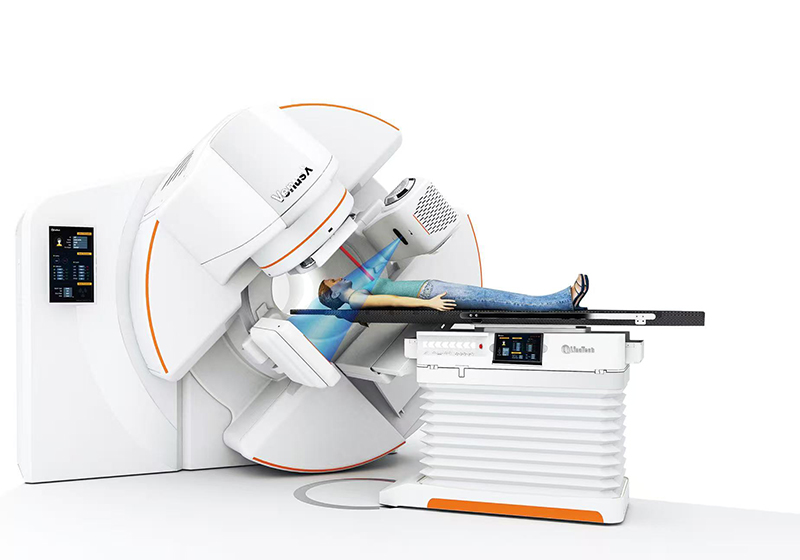
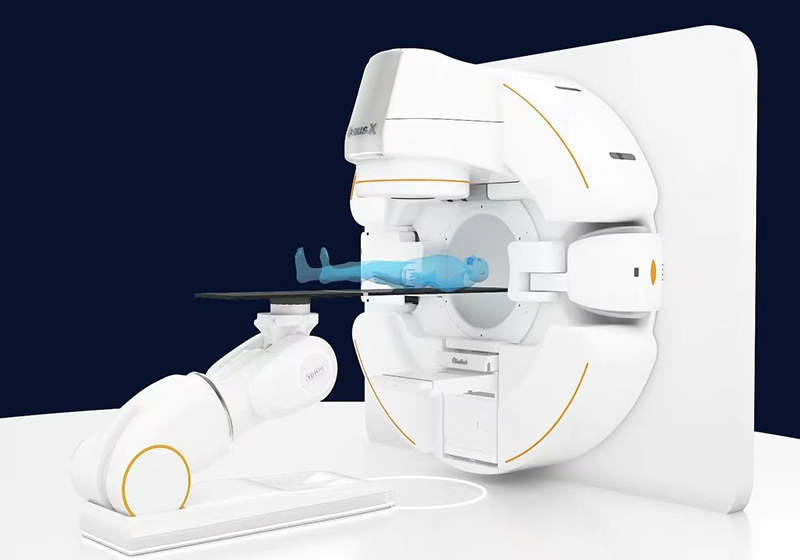
I. What is Linear Accelerator Radiotherapy?
A linear accelerator is a medical device that uses an electromagnetic field to accelerate electrons to near the speed of light, then generates high-energy X-rays or electron beams to precisely irradiate tumors.
👉 The core objective can be summarized in one sentence: Kill tumors with the maximum dose while minimizing damage to normal tissue.
⸻
II. How Does a Linear Accelerator “Kill” Tumors?
🔬 Mechanism of Action (Simplified Version)
• High-energy rays → Break tumor cell DNA
• Tumor cells:
• Poor DNA repair ability
• Rapid division → More prone to death
• Normal cells:
• Strong repair ability
• Recovery is possible through fractionated irradiation
📌 Therefore, radiotherapy is usually performed in multiple fractionated irradiations.
⸻
III. Which tumors can a linear accelerator treat?
✅ Common Indications
Covering almost 70–80% of cancer patients
Solid Tumors
• Lung Cancer (NSCLC/SCLC)
• Breast Cancer
• Prostate Cancer
• Head and Neck Cancer (Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, Oropharyngeal Carcinoma)
• Brain Tumors (Gliomas, Metastases)
• Cervical Cancer / Rectal Cancer
• Liver Cancer (in conjunction with precision radiotherapy)
Others
• Bone Metastasis Pain Relief
• Postoperative Adjuvant Radiotherapy
• Radical Treatment for Inoperable Patients
⸻
IV. What are the “Advanced Modes” of Modern Linear Accelerators?
This is the core of the technological gap 👇
1️⃣ IMRT (Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy)
• Different doses at each angle
• Strong tumor-reducing ability
• Protects the spinal cord, optic nerve, etc.
2️⃣ VMAT (Volume Modulated Amplitude Radiotherapy)
• The machine rotates while delivering the radiation
• Short treatment time (2–5 minutes)
• More patient comfort
3️⃣ IGRT (Image-Guided Radiotherapy)
• CT/CBCT calibration before each irradiation
• Error < 1–2 mm
4️⃣ SRS/SBRT (Stereotactic Radiotherapy)
• High dose, fewer sessions
• Suitable for:
• Brain metastases
• Early-stage lung cancer
• Oligometastatic tumors
📌 This type of technology is close to “precision strikes without a scalpel”
⸻
V. A complete linear accelerator treatment process
🧭 Standard procedure
1️⃣ Positioning CT
• Fix the patient’s position (thermoplastic membrane/ 1. Vacuum mat
2. Target delineation
• Tumor area (GTV / CTV / PTV)
• Organs at risk (OAR)
3. Physical therapy planning
• Dosage calculation + optimization
4. Treatment implementation
• 5 times per week
• 4–7 weeks (depending on protocol)
5. Efficacy & side effect monitoring